Understanding Malware & How to Detect it
- Home
- Hack or Not
- Understanding Malware & How to Detect it

- Mikey Ryu
- September 20, 2023
- 0
Understanding Malware & How to Detect it
Detecting Malware
In today’s interconnected world, the threat of malware looms large. Malicious software, or malware for short, is a pervasive and constantly evolving menace that can wreak havoc on your digital life. From stealing your sensitive information to rendering your computer useless, malware comes in various forms and can target anyone. In this blog, we will delve into the world of malware, exploring its different types, how it spreads, and most importantly, how to detect it to protect your digital assets.
What is Malware?
Malware is an umbrella term that encompasses a wide range of malicious software programs designed to infiltrate, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems, networks, and data. These programs are created by cybercriminals with nefarious intent and can cause significant harm if left unchecked.
Types of Malware
Malware comes in many flavors, each with its own distinct characteristics and purposes. Here are some of the most common types:
- Viruses: Viruses attach themselves to legitimate files or programs and replicate when the infected file is executed. They can spread to other files and devices through infected files.
- Trojans: Named after the mythological Trojan horse, Trojans are malware disguised as legitimate software. They often come attached to seemingly harmless downloads or email attachments.
- Worms: Worms are standalone malware programs that can spread independently. They exploit vulnerabilities in a network or system to replicate and infect other devices.
- Ransomware: Ransomware encrypts your files and demands a ransom in exchange for the decryption key. Paying the ransom is not recommended, as it does not guarantee the return of your files and encourages cybercriminals.
- Spyware: Spyware secretly monitors your activities and collects sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card details, and personal data, which is then sent to the attacker.
- Adware: Adware floods your system with unwanted advertisements, often generating revenue for the attacker through pay-per-click schemes.
- Keyloggers: Keyloggers record your keystrokes, enabling cybercriminals to capture login credentials and other sensitive information.
- Rootkits: Rootkits hide themselves deep within your operating system, making them difficult to detect. They often grant unauthorized access to the attacker.
- Botnets: Botnets are networks of compromised computers, often used to launch coordinated attacks, send spam emails, or carry out other malicious activities.
How Does Malware Spread?
Understanding how malware spreads is crucial in preventing infections. Here are some common methods:
- Phishing: Cybercriminals use deceptive emails, messages, or websites to trick you into downloading or executing malware.
- Drive-by Downloads: Malware can be automatically downloaded and installed when you visit a compromised website or click on a malicious link.
- Infected Attachments: Malware-laden attachments in emails are a common vector. Opening these attachments can initiate an infection.
- Software Vulnerabilities: Outdated or unpatched software can have vulnerabilities that malware exploits to gain access to your system.
- Removable Media: Malware can spread through infected USB drives or other removable media when inserted into your computer.
- Peer-to-Peer File Sharing: Sharing files on P2P networks can expose you to malware if you download files from untrusted sources.
- Malvertising: Malicious advertisements on legitimate websites can deliver malware when clicked.
How to Detect Malware
Now that we’ve covered what malware is and how it spreads, let’s explore how to detect it. Early detection is key to minimizing the damage malware can cause.
Use Antivirus Software
Installing reputable antivirus software is one of the most fundamental steps in detecting and preventing malware infections. These programs scan your system for known malware signatures, suspicious behaviors, and vulnerabilities. Keep your antivirus software updated to ensure it can detect the latest threats.
Enable Firewalls
Firewalls act as a barrier between your computer and potential threats from the internet. They monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic and can block suspicious connections. Most operating systems come with built-in firewalls that you should enable.
Regularly Update Software
Keeping your operating system, applications, and plugins up to date is crucial. Developers release updates to patch security vulnerabilities that malware can exploit. Configure your software to update automatically if possible.
Be Cautious of Email Attachments and Links
Exercise caution when receiving emails with attachments or links, especially if they come from unknown or suspicious sources. Avoid opening attachments or clicking on links in unsolicited emails. Verify the sender’s identity if you have any doubts.
Download from Trusted Sources
Only download software, apps, and files from reputable sources. Avoid downloading pirated software, as it often comes bundled with malware. Stick to official app stores and trusted websites.
Monitor System Performance
Malware can slow down your computer and cause unusual behavior. Keep an eye on your system’s performance and look out for signs such as excessive CPU or memory usage, unexpected crashes, or unexplained network activity.
Educate Yourself
Awareness is your best defense against malware. Educate yourself and your employees or family members about the risks of malware and safe internet practices. Regularly update your knowledge about emerging threats and attack vectors.
Use Behavioural Analysis
Advanced antivirus solutions use behavioral analysis to detect malware by analyzing a program’s actions rather than relying solely on known signatures. This helps identify zero-day threats that haven’t been seen before.
Regularly Back Up Your Data
In case of a malware infection or a ransomware attack, having up-to-date backups of your data can save you from losing valuable information. Ensure your backups are stored securely and can be restored when needed.
Employ Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) can monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and alert you to potential threats. They are especially useful for businesses and organizations with large networks.
Seek Professional Help
If you suspect a malware infection that you can’t handle on your own, seek the assistance of cybersecurity professionals. They have the expertise and tools to thoroughly analyse and remove malware from your systems.
Here’s Some Examples
We received this message a while ago on the 11th of September.
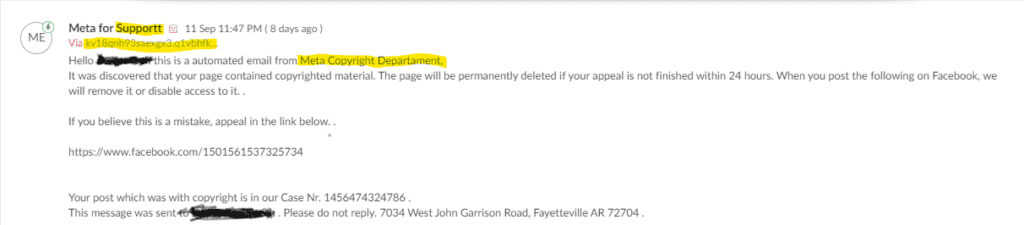
There are many things that indicate that this is not a legit email from META themselves, things such as spelling mistakes and who it was sent by tell us all we need to know, in fact by copying the link and placing it into some messaging software can highlight that it is not an actual message regarding a copyright case.
When pasting it to send it to someone else it says something rather interesting….
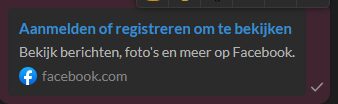
Now seeing this you can tell 100% that it’s not a legitimate link.
Conclusion
Malware is a persistent threat that evolves alongside technology. Understanding its various forms and how it spreads is crucial for protecting your digital life. By following best practices such as using antivirus software, keeping your software up to date, and being cautious online, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to malware. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and stay safe in the digital world.
Search
Categorys
- Branding (12)
- Business Growth Guides (3)
- Business Insights (3)
- Content Marketing (43)
- Domain Authority (19)
- Email Marketing (28)
- Google Analytics & Search Console (5)
- Hack or Not (2)
- Hero Host News (0)
- Inbound Marketing (32)
- Lessons From Asia (40)
- Marketing Guides (11)
- Martial Arts Journey (14)
- Outbound Marketing (8)
- Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) (41)
- Social Media Marketing (38)
- Web Design (20)
- Website Hosting (4)
- Wordpress (2)




